
|
<<<
www.interlibrary.narod.ru |
|
|
Khod’kov A.E. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The New Cosmogonic Theory (NCT)
about regularities of genesis of different
in qualitative composition atomic matter
in the process of starry evolution
|
Introduction The
first information about elaboration of NCT was advertised in 1989 in the
paper .The Problems of cosmic thermo-percussive influences on the Earth in a
view of the NCT. [1]. The
purpose of this information is to show on instance of development of a
double-star the Jupiter.Sun in what manner it could be analysed how the
differences in qualitative composition of atomic matter appears inevitably. The
theoretical kernel for analysis of cosmogenesis after a phase of star's
origin from Hydrogen accumulation is the conception of correlated development
of chemical elements periods and satellite-planets which was suggested by
geologist Khod'kov A. E. in 1943.1945. From it`s state the appearance of
atoms of all chemical elements more complex than Hydrogen atom takes place
within stars, including the Sun, and proceeds as a cyclic process at which
the formation of each element`s period completes with an explosion and a
flash of a "new" star and removal of it`s outer cover with any part
of synthesized atomic substance into it's vicinity. These equatorial
revolving portions of thrown cover later serves to form a new
satellite-planet or a wreath of asteroids. This
conception increased to the NCT thanks to discovery by Knod`kov in 1985 a new
cosmic phenomenon . thermo-percussive
influences of the explosive waves of the Sun (TPIEWS) upon the Earth. They
provoked a global tectonic re-structuring of earthy lithosphere and
repeatedly in the past forsaked becoming diastrophic traces, excelling at
sequence of ages and destructive power. 1.
Initial statements: .
The principle of the basic difference between the evolving constituent parts
of star systems and the derivatives of their evolution. The first
considerably alter in the course of development their radii, mass and angular
velocity of their own rotation after the regular loss of exploding cover,
while their derivatives are incapable to do it [ 1]. .
The thesis about an impulse of rotation of each thrown down cover and then of
satellite which is stipulated by corresponding to moment of flash parameters
of paternal star. To sum up whichever star rotates most speedily than all
it`s derivatives [2]. .
The statements following from Roche`s law that the process of interdependent
development of double-component tight evolving star system can be accompanied
by the usurpation of the derivatives of one of the stars by the other [4, 5]. .
The treating of main diastrophisms in the tectonic history of thc Earth:
Pacific, Karelian and Saamian . as
the repercussion of the last three global TPIEWS upon the Earth at 0,22,
before 2,0 and 3,7 billion years ago and chronology of the completing of the
5-th, 4-th and 3-d periods of Sun atomic synthesis [1,6,7]. 2.
The mechanical parameters of the Solar system in a view of they genetic
analysis [2] With
help of the genetic analysis of the Solar system mechanical parameters it
were scrutinized in first time the angular velocities of celestial bodies in
comparison of own rotation with turning around. At enormous their
incongruous, as by the Neptune, Uranus, Saturn, Jupiter, at once may be
exposed a faded stars because they could not to be formed from thrown down
starry covers. The
structures and quantities of the earth group planets rotation and circulation
mechanical parameters, as it was found, cannot belong to the system of
singular evolving star . the
Sun, but it reflects the existence and interaction of double star. It became
evident that the supposition that the Sun is a single star doesn't allow to solve the problem of the origin of the Solar system. In
fact, among sunny derivatives must be those celestial bodies that rotate more
slowly than the Sun (during more 25 astr. days). It is Mercury, Venus and
Moon. But
the Earth and Mars, which rotate during about 1 astr.
day, are the derivatives of the Jupiter, captured by
the Sun. Therefore the last stage of Solar system development is considerably
tied with the evolution of the double-star system Jupiter.Sun: this
demonstrates by mechanical parameters of their derivatives and other facts.
Among them . the usurpation
of the third sunny derivative the Moon by the sixth Jupiter's derivative the
Earth. The
most common summary of the genetic analysis is that our Solar system is
heterogeneous and of different age; it is a kind of a combination of faded,
finished their evolution stars and starry derivatives, that
came into existence at different times and passed through their own way of
development. 3.
The peculiarities of starry evolution as the process of interrupting atomic
synthesis [3] It
was founded one-significantly that starry life flies in a broken voice and
has a cyclic character on account of interruption of cosmogenesis and change
of regime of natural nuclear synthesis by leaps and bounds. Then
a number of stages of starry development and quantity of derivatives cosmic
bodies appear stipulated by number of steps of transition to new qualitative
structures of atom's basis in a moment of forming of last element in a period
or row. The
regularity of this process for different components of double star has a
peculiarities connected with distinction of their mass, angular velocity of
rotation and intensity of magnetic field. Periodic
throw down of outer covers leads to following jumping changes in a star: for
decrease of it's mass and capacity to light, increase of it`s velocity of
rotation, change of spectral types of it's eradiation and replace of zone of
stellar transformation deep from surface. And the spectral type of starry
eradiation is determined by the number of synthesized periods: the Sun as a
typical star of the Main Sequence completed 5 periods and coloured into 5-th
type (G). The
equatorial portions of covers, thrown off by star, are reforming (during . 500 million years) into secondary bodies-satellites
with complicating of chemical element`s composition and increasing of own
rotation at next in turn of cycle number. Therefore
equivalency in conditions of secondary bodies origin could not be realized
through the different qualitative composite of their matter and, as shown in
[2], through the genetic difference in mechanical parameters of their
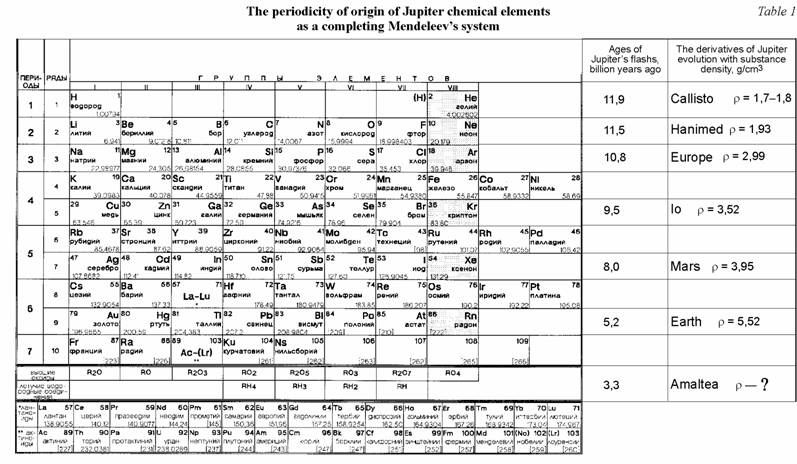
rotation. Achieved by authors in [1.3, 6, 7] classification of Jupiter.s and sunny derivatives at genetic rotatory characteristics exposes their conformity with time of their origin and inevitably detects the regular increase of density of their matter with the decrease of their age. This conclusion illustrates by tables 1 and 2. |
|
The
periodicity of origin of Sun chemical elements |
|||||||||||
|
reflecting
in geologic cycles and derivatives of sunny evolution |
|||||||||||
|
Table 2 |
|||||||||||
|
Periods |
Rows |
Groups |
Ages of Sun flashs million years ago and
diastrophisms |
The tracts of thrown off outer shells or the derivation
of Sun cycles, density, g/cm3 |
|||||||
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
He |
5001 |
in
possible, comet |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
ρ=1.4 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
4567 |
carbonaceous asteroids
and Fobos |
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
ρ=2.2 |
|
|
3 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
siliceous asteroids and Moon |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
Si |
|
|
|
|
3699 Saamian |
ρ=3.3 |
|
|
|
29 |
36 |
43 |
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fe |
2831 |
iron
asteroids |
|
|
|
57 |
64 |
71 |
78 |
|
|
|
78 |
Kenoran |
ρ=4 |
|
4 |
|
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
Ge |
|
|
|
|
1963 |
Venus |
|
|
|
85 |
92 |
99 |
106 |
|
|
|
|
Karelian |
ρ=4.9 |
|
|
|
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
|
Mercury |
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
Zr |
|
|
|
Ru |
1095 Greenville |
ρ=5.3 |
|
|
|
107 |
109 |
111 |
113 |
116 |
120 |
127 |
134 |
|
|
|
5 |
|
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
Sn |
|
|
|
Xe |
227 Pacific |
future Volcano |
|
|
|
141 |
148 |
150 |
152 |
154 |
157 |
160 |
162 |
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
8 |
|
|
|
Hf |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
163 |
165 |
167 |
169 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LITERATURE 1. Khod'kov A. E.,
Vinogradova M. G. The Problems of cosmic thermo-percussive influences on the
Earth in a view of the New Cosmogonic Theory // Theoretical and applied problems
of geology and hydro-geology. Leningrad. AUISR of Galurgy. 1989. P. 143.165. 2. Vinogradova M. G. The
genetic analysis of peculiarities of planet`s system developnent in tight
double-star the Jupiter-Sun. International Academy (IAICC). Messenger N 12-1s
(December). St.-P. 2000. P. 3.12. 3. Khod`kov A. E.,Vinogradova M. G. The basis for understanding of
interrupted cosmogenesis . in
the interconnection with periodicity of chemical elements // The problems of
space and time in natural science. Ser. The Problems of the Universe
Investig. iss. 16. St.-P. Rus. Ac. of Science. 1993.
P. 215.223. 4. Lipunov V. M. In the
world of double stars. 5. Drobyshevskey E. M.
The planet systems as a breaking point or collateral product of formation of
double systems. Messenger of Astronomy. V.21. N 4. 1987. 6. Khod`kov A. E.,
Vinogradova M. G. From an atom of Hydrogen to the Solar system (3-d issue,
revised and completed). St.-P. Nedra Publishers. 1998. 192 p. 7. Khod`kov A. E.,
Vinogradova M. G. About the scape`s problems of natural (physical) science.
St.-P. Nedra Publishers. 1997. 192 p. 8. Khod.kov A.E.,
Vinogradova M.G. The bases of Cosmogony: about origin of worlds, the
Sun and the Earth. St.-P. Nedra Publishers. 2004. 336 p. |